M1Pram
M1Pram, a unique formulation of amyline and insulin analogs with a proven track record
Adocia has developed M1Pram to enable patients affected by both diabetes and overweight or obesity to address weight management and glycemic control as co-primary targets of care.
Today, more and more people are affected by both diabetes and obesity, and “Diabesity” is now considered a pandemic. The two diseases are closely interlinked, one being both cause and consequence of the other. Pancreatic beta cells produce two key hormones: insulin and amylin, involved in both glycemia regulation and weight control. It is therefore crucial to restore the physiologic equilibrium, what can be achieved by M1Pram, a fixed-dose combination of insulin and amylin analogs.
M1Pram is a ready-to-use co-formulation of pramlintide (an amylin analog) and M1 (a mealtime insulin analog). Injected by pen at mealtime, as any prandial insulin, M1Pram has demonstrated to maintain a good glycemic control, while triggering significant weight loss, associated with effects on satiety and a reduction of the insulin dose.
M1Pram has successfully completed Phase 2 studies and is available for out-licensing.
Today, more and more people are affected by both diabetes and obesity, and “Diabesity” is now considered a pandemic. The two diseases are closely interlinked, one being both cause and consequence of the other.
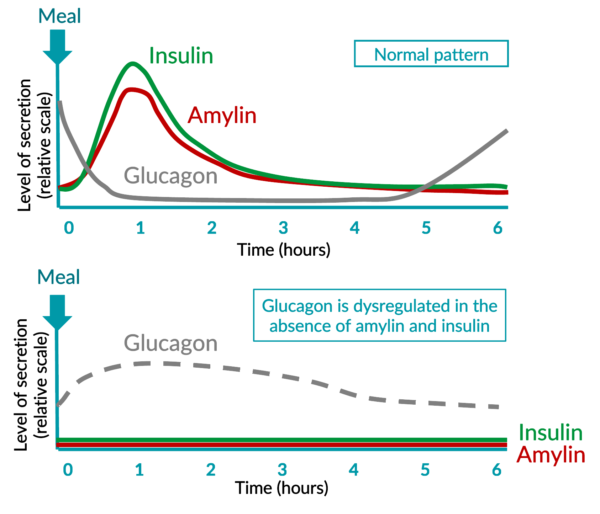
In people who do not have diabetes, insulin is secreted synchronously and acts in synergy with other hormones, such as amylin, to control glycemia. In people with diabetes, ultimately, neither insulin nor amylin are secreted.
Insulin allows the body to use sugar as energy, to store it when not needed and acts via an anabolic pathway. Amylin acts on both central nervous system and peripheric levels and plays a role on satiety, well-being and glycemic control.
It is therefore possible that the use of insulin alone cannot address all the metabolic deficiencies related to diabetes. And people with diabetes shouldn’t have to choose between controlling their glycemia and their weight.
M1Pram, a fixed-dose combination of an amylin analog (Pramlintide) with an analog of insulin (M1, A21G analog of human insulin, and metabolite of insulin glargine), could therefore prove to be an elegant solution to maximize the medical benefits on both glycemic control and weight management.
Adocia used its formulation expertise to overcome a technological challenge and provide a stable formulation of the two hormones (otherwise incompatible), to be administered at mealtime via a pen, as any prandial insulin.
M1Pram ready-to-use solution has proven to maintain a good glycemic control and to trigger significant weight loss, and should ensure high patient compliance and health costs control.
M1Pram, a unique formulation of amylin and insulin analogs with a proven track record
M1Pram is a ready-to-use, fixed-dose combination of:
- M1, the A21G analog of human insulin exhibiting an action profile of a mealtime insulin. It is also the major metabolite of insulin glargine (commercialized as Lantus®, Sanofi). As a result, millions of insulin glargine users worldwide have been exposed for years to M1. It is therefore a well-known insulin with an established action and tolerance profile.
- Pramlintide is a rapid acting amylin analog FDA-approved since 2005 for type 1 and type 2, as an adjunct to insulin.
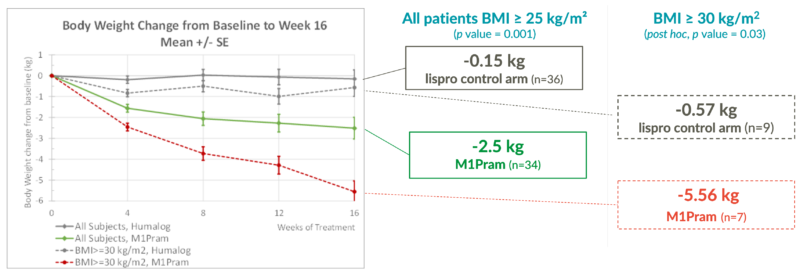
CT041: Phase 2 study – M1Pram vs. lispro (Humalog®) – type 1 diabetes – 16 weeks ambulatory
M1Pram has been through extensive clinical trials.
Latest Phase 2 results (and post-hoc analysis) were positive and M1Pram demonstrated after 16 weeks of treatment:
- Weight loss effects: -5.5kg in people with type 1 diabetes and a body mass index greater than 30kg/m², and weight loss had not plateaued by the end of the study
- Good glycemic control: efficacy comparable to that obtained with the commercial reference insulin Humalog® (Eli Lilly)
- Sparing effect on insulin consumption: prandial insulin daily dose reduced by -21%
- Patients’ satisfaction: better control of appetite expressed in patient satisfaction scoring (82.4% with M1Pram vs. 43.2% with Humalog®)
- Good tolerance profile
M1Pram, a unique formulation endorsed by the scientific community

“I believe this combination has the potential to finally deliver on the promise of pramlintide for a large number of patients, by addressing the significant unmet need for tighter post-prandial control and lower glycemic variability without the burden associated with another product and a higher number of injections.”
Professor Robert Ratner, MD, Georgetown University School of Medicine, Washington DC.

“Adocia has developed a product which combines an insulin analog together with pramlintide in a stable mixture, so that only a single pre-meal injection is needed. The glycemic results with M1Pram to date are quite promising as is the observed weight loss, which is important given the characteristics of the population taking prandial insulin. I look forward to the next series of clinical trials.”
Professor Jay S. Skyler, MD, University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine, FL.

“This trial confirmed the strong reduction of the postprandial glucose excursion previously observed in a clinical trial with M1Pram. Furthermore, the outpatient period showed improvement in time in target glycemic range without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia, as well as an improvement in weight control, two key medical benefits for people with type 1 diabetes.”
Professor Thomas Pieber, MD, Medical University of Graz, Austria.